Blog 2: Disabilities , Savia Saffo

Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD)
By: Savia Saffo
What is Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD)
It's a neurological and developmental condition that impacts a person's ability to learn, behave, connect with others, and communicate. Autism is classified as a "developmental disorder" even though a diagnosis can be made at any age. This is because the majority of symptoms usually manifest in the first two years of development (NIMH, 2024). Individual differences in the spectrum of symptoms and their intensity might be significant. This blog post will go into great detail on the signs and symptoms of ASD and how they affect growth, cognitive abilities, and emotional health.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/What-are-the-three-levels-of-autism-260233-5baab02fc9e77c002c390bd2.png)
Symptoms
Autism Spectrum Disorder is typified by a variety of symptoms that can manifest in unique ways in every person.
- Social Communication Challenges: Inability to participate in standard back-and-forth dialogues; decreased expression of interests or feelings; inability to recognize and react appropriately to social cues.
- Repetitive behaviors: Include insisting on sameness, following strict routines or rituals, and engaging in repetitive motions or vocal patterns (such as hand flapping or echolalia).
- Hyper- or hypo-reactivity to sensory input: Such as an atypical sensitivity to sounds, lights, textures, or flavors, is referred to as sensory sensitivity.
- Interests that are restricted: A strong concentration on a single subject or activity, frequently at the expense of other interests.
- Delays in language acquisition: Challenges in creative play, and postponed motor skill milestones are examples of developmental delays. At their 9-, 18-, 24-, or 30-month well-child visits, the American Academy of Pediatrics advises all parents to screen their children for developmental delays (NIMH, 2024). In particular, the 18- and 24-month well-child visits should include an autism screening.
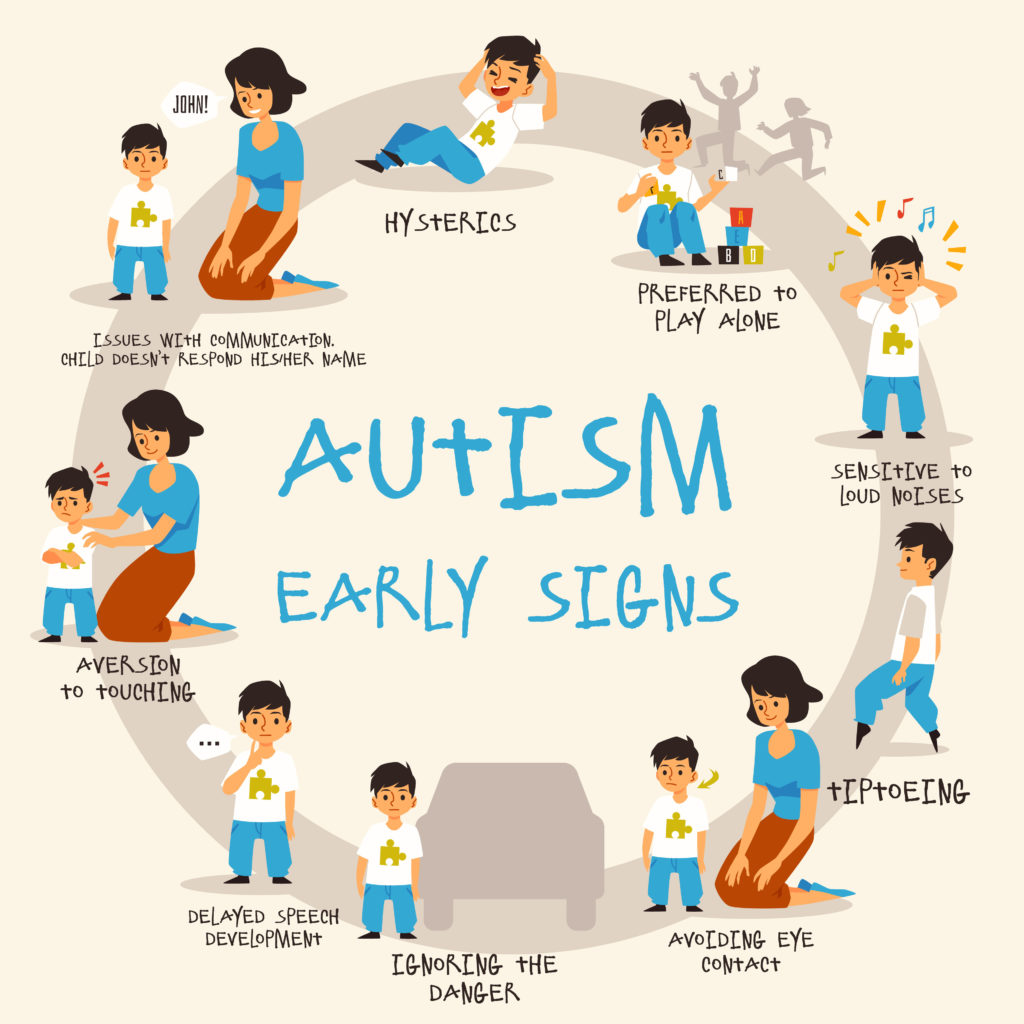
Disability Impacts Development
From early childhood through maturity, an individual's development can be greatly impacted by ASD. Early developmental effects frequently include issues creating relationships and participating in social play, delays in speech and language learning, and difficulties developing fine and gross motor abilities. Because children with ASD may find it difficult to learn in conventional classroom environments that do not meet their specific needs, these developmental delays can have an impact on academic achievement and school preparedness (Al Jaffal, 2022). These developmental effects may persist into adolescence and adulthood in people with ASD as they age. Particularly hampered social development might make it difficult to establish and maintain sexual relationships, friendships, and workplace social norms. More independence and a higher quality of life can be created by providing lifelong support and intervention to help lessen some of these developmental obstacles.

Cognitive Skills Affected by Disability
- The cognitive capacities of people with ASD might differ greatly. While some people may be intellectually disabled, others may be intelligent enough to be above average. Typical cognitive difficulties linked to ASD include:
- Having trouble organizing, planning, and finishing work is a sign of an executive functioning deficit. Both daily living skills and academic achievement may be impacted by this.
- Theory of Mind: The difficulty of appreciating that people think, feel, and see things differently from oneself. Misunderstandings and societal problems may result from this (Hajr et al., 2022).
- Attention & Focus: Diverse people have varying attention spans; some are hyperfocused on particular hobbies, while others have trouble paying attention (Finch et al., 2022).
- Customized educational strategies and interventions are required to enhance cognitive development because these cognitive problems can have an impact on learning and adaptive functioning.
Living with ASD: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=AYnZm8DEke4&themeRefresh=1
Emotions Affected by Disability
The effects of ASD on the emotions might be severe. Due to their challenges comprehending and negotiating social settings, people with ASD may feel more anxiety, despair, and frustration. It can be difficult to control one's emotions, which can cause shutdowns or meltdowns in reaction to stressful or overpowering stimuli.

Furthermore, feelings of loneliness and low self-esteem can be made worse by the social exclusion and bullying that people with ASD frequently experience. Supportive therapies, like social skills training and cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT), can assist people with ASD in improving their mental health and coping skills (White et al., 2018).
Emotional Identification and Communication: The inability to identify and understand feelings in others as well as in oneself is one of the main emotional problems that people with ASD encounter. Theory of Mind deficiencies may be the cause of this problem. Theory of Mind is the capacity to recognize other people think, feel, and see things differently from oneself. People with ASD may thus find it difficult to interpret facial expressions and social cues, which can result in miscommunication and social isolation. Many people with ASD have hypersensitive emotional responses, which can lead to shutdowns or meltdowns when they can't handle stressful events or stimuli. This can be especially difficult in situations when their demand for routine or their sensitivity to certain stimuli are not met (Fuld, 2018).
Depression and Anxiety:Depression and anxiety are frequent co-occurring disorders in people with ASD. Persistent tension and anxiety may be exacerbated by the ongoing challenge of navigating social interactions and sensory overload. Research has indicated that, in contrast to their neurotypical counterparts, people with ASD are more prone to exhibit symptoms of anxiety disorders and depression (White et al., 2018). Emotional distress can be exacerbated by mental health problems, making it more difficult to control emotions and engage in social interactions.
References
Al Jaffal M. (2022). Barriers general education teachers face regarding the inclusion of students with autism. Frontiers in psychology, 13, 873248. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyg.2022.873248
Finch, T. L., Mackintosh, J., Petrou, A., McConachie, H., Le Couteur, A., Garland, D., & Parr, J. R. (2022). "We couldn't think in the box if we tried. We can't even find the damn box": A qualitative study of the lived experiences of autistic adults and relatives of autistic adults. PloS one, 17(3), e0264932. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0264932
Fuld S. (2018). Autism Spectrum Disorder: The Impact of Stressful and Traumatic Life Events and Implications for Clinical Practice. Clinical social work journal, 46(3), 210–219. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10615-018-0649-6
Hajri, M., Abbes, Z., Yahia, H. B., Jelili, S., Halayem, S., Mrabet, A., & Bouden, A. (2022). Cognitive deficits in children with autism spectrum disorders: Toward an integrative approach combining social and non-social cognition. Frontiers in psychiatry, 13, 917121. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyt.2022.917121
NIMH. (2023). Autism spectrum disorder. National Institute of Mental Health. https://www.nimh.nih.gov/health/topics/autism-spectrum-disorders-asd#:~:text=Autism%20spectrum%20disorder%20(ASD)%20is,first%202%20years%20of%20life
White, S. W., Ollendick, T. H., & Albano, A. M. (2018). Building a bridge between CBT researchers and practitioners: Clinical trial meets clinical practice in the treatment of anxious youth. Behavior Therapy, 49(1), 20-36. DOI: 10.1016/j.beth.2017.07.003
Comments
Post a Comment